Understanding the Major Iberian Peninsula Power Outage
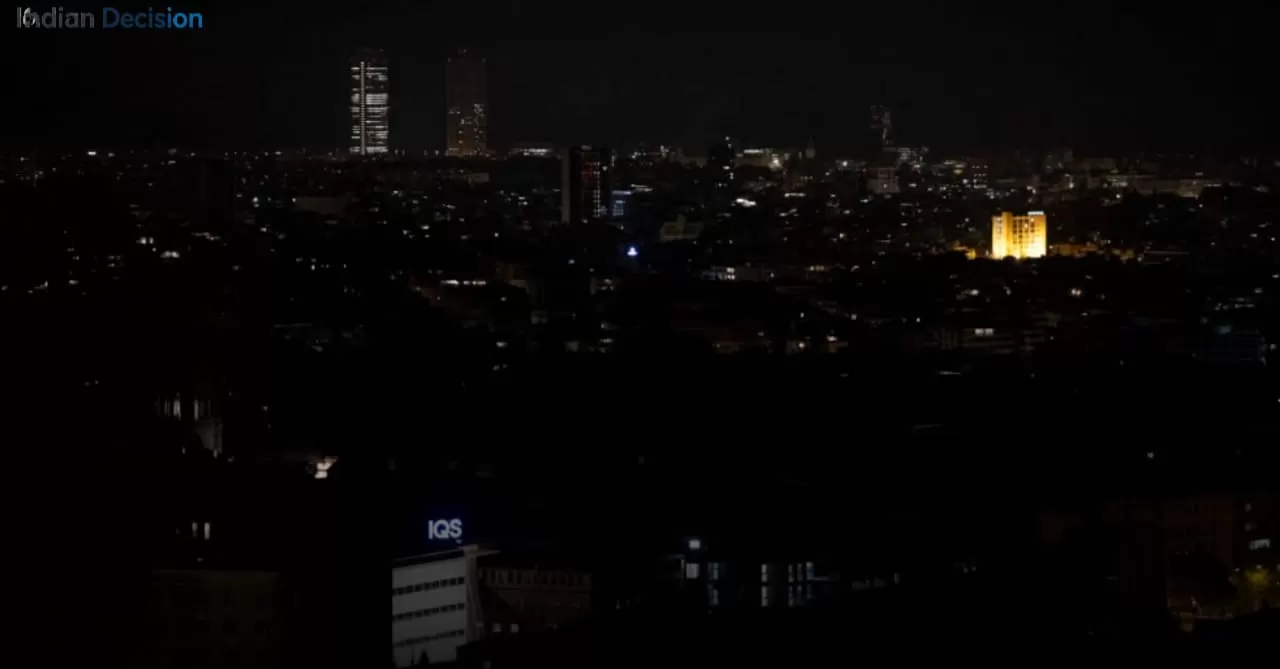
A significant power outage has impacted large portions of Spain and Portugal, leaving millions without electricity and disrupting daily life across the Iberian Peninsula. This large-scale event, which began in the morning hours, has triggered widespread concern and emergency responses from national grid operators.
The simultaneous nature of the blackout across both nations points to a disruption within the interconnected electricity grid they share. Authorities are working tirelessly to first stabilize the network and then restore power in a coordinated manner. The focus is on identifying the root cause while managing the cascading effects of the grid failure. This incident highlights the critical importance and vulnerability of interconnected energy systems in modern Europe.
Today's Live Update: Current Situation on the Ground
As of today, the situation remains fluid. Power has been successfully restored to several key metropolitan areas, including central Madrid and Lisbon, after hours of extensive work by technicians. However, many rural and suburban regions in both countries are still experiencing blackouts. Reports from social media and local news outlets indicate significant disruptions to rail services, with delays and cancellations on commuter lines. Water supply systems, which rely on electric pumps, have been affected in some towns, prompting local authorities to distribute bottled water.
The Spanish and Portuguese governments have held an emergency press conference, urging citizens for patience and assuring them that restoring full power is the absolute top priority. A full investigation into the cause has been officially launched.
The Root Cause: What Triggered the Grid Failure?
While the official investigation is ongoing, preliminary reports from Red Eléctrica de España and Redes Energéticas Nacionais point to a catastrophic cascade failure. The initial trigger is believed to have been a major fault at a key high-voltage substation in northern Spain. This fault caused a sudden, massive drop in frequency on the Iberian grid. To protect themselves from damage, other power generation plants and transmission lines automatically disconnected, creating a domino effect that collapsed the network.
This type of failure is a known risk in interconnected systems, where the sudden loss of a critical node can overwhelm the built-in safety protocols. It was not an issue of insufficient power generation but rather the instability of the transmission infrastructure itself that led to the widespread blackout.
Immediate Impact and Response to the Blackout
The immediate impact of the power cut in Spain and Portugal has been profound. Airports implemented emergency protocols, leading to flight delays and diversions. Hospitals switched to backup generators to maintain critical care. Cellular networks were strained, and internet services were spotty as backup power at data centers was tested. The response was swift from emergency services, with a primary focus on public safety and securing essential services. Key actions taken included.
- Activation of National Emergency Protocols: Both governments activated their respective civil protection units to coordinate the response.
- Prioritization of Critical Infrastructure: Grid operators worked to first restore power to hospitals, water treatment plants, and communication networks.
- Public Communication Campaigns: Officials have been using radio, social media, and other available channels to provide updates and safety advice to the public.
- Cross-Border Collaboration: Spanish and Portuguese grid operators are in constant communication to ensure a synchronized restoration process.
Historical Context and Grid Vulnerability
This is not the first major disturbance for the Iberian electricity system, though its scale is significant. The Spanish-Portuguese grid, while interconnected, has historically had limited connectivity to the wider European grid, making it something of an energy island. This isolation can sometimes make the network more susceptible to internal shocks, as it has less capacity to import power to stabilize a frequency drop from neighboring countries.
Recent investments have been made to increase interconnection with France, but the system's resilience is still being tested. This event will undoubtedly lead to a serious re-evaluation of grid infrastructure, investment in modernization, and the robustness of fail-safe mechanisms to prevent a single point of failure from causing a regional collapse.
The Path to Restoration and Future Prevention
Restoring power after a complete blackout is a meticulous and gradual process known as a black start. It involves carefully bringing power generation plants online and slowly re-energizing sections of the grid to avoid causing further damage. The process is expected to continue for several more hours, with full restoration potentially taking much of the day. Looking ahead, this large-scale power outage in Portugal and Spain will force a major policy discussion. Key areas for future prevention will likely include.
- Accelerating investments in grid modernization and smart grid technologies.
- Enhancing the physical security of critical substations and infrastructure.
- Increasing the capacity of interconnections with the European grid to provide greater stability.
- Reviewing and updating the automatic load-shedding and protection systems to make them more resilient.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What caused the power outage in Spain and Portugal?
The primary cause appears to be a cascade failure initiated by a fault at a major substation in northern Spain. This caused a rapid frequency drop, triggering automatic shutdowns across the grid that led to the widespread blackout.
Is the power back on in Spain and Portugal?
As of the latest updates, power has been restored to major cities like Madrid and Lisbon, but many other areas are still waiting. The restoration is an ongoing process and full recovery may take time.
How long will the power outage last?
While the worst is over, complete stabilization and full restoration for all affected areas could take several more hours. Authorities are prioritizing critical services first.
Was this a cyberattack on the power grid?
Officials from both countries have stated that there is no evidence to suggest a cyberattack. The initial assessment points to a technical failure in the grid infrastructure.
Which areas were most affected by the blackout?
The outage was widespread across both nations. Major urban centers and their surrounding regions in both Spain and Portugal experienced the blackout, with rural areas often being the last to be reconnected.
What should residents do during the power outage?
Residents are advised to stay informed via battery-powered radio, conserve phone battery, check on vulnerable neighbors, and avoid using elevators. Follow official guidance from local authorities.
How can such a blackout be prevented in the future?
Prevention requires modernizing aging grid infrastructure, improving interconnections with other European countries, and enhancing the resilience of automatic protection systems to prevent cascade failures.
Conclusion: A Wake-Up Call for Energy Infrastructure
The major power outage across Spain and Portugal serves as a stark reminder of the fragility of our interconnected energy systems. While the immediate priority remains restoring power to every last customer, the long-term conversation must focus on building a more resilient and secure grid. This event will likely catalyze significant investment and policy changes to ensure that the lights stay on across the Iberian Peninsula. For the latest official updates, citizens are encouraged to monitor the channels of their national grid operators and government emergency services. The road to full recovery continues, but the lessons learned today will shape a more reliable energy future.